“How do I balance a shaft?” seems like a fairly straightforward question, but there are a number of things that we need to understand first. Here we look at a number of key concepts that need to be understood in order perform balancing.
What does balance mean?
Well broadly speaking to balance a shaft, mass must be added or removed at certain angles. The concept being that the centre of gravity and rotational centre of the shaft will be equal when the shaft is balanced.
Can a shaft be balanced at several speeds or across a speed range?
If a shaft is made from a uniform density material the whole way round its radius and it was perfectly rigid then it could be considered in balance at any speed. However it is not possible to produce a shaft with uniform density round its radius and along its length, further it is not possible to produce a shaft that is perfectly rigid, therefore at different speeds the shaft would bend in different ways. At certain frequencies certain modes would be excited, thus the physical shaft centre points, at certain positions, would move and the centre of gravity of the shaft would move as well at these points. At these points, which are themselves moving along the shaft continually as the speed changes. For this reason it is not possible to balance a shaft for all speeds, the balance is linked to the dynamics of the whole system, not just the shaft itself.
What sensors are required to perform shaft balancing?
Quite simply a once per revolution tachometer signal and at least a uni-axis accelerometer, it would be recommend to use two uni-axis accelerometers mounted at a balance measurement position in the perpendicular and vertical planes with respect to the shaft.
What is a balance measurement position?
A balance measurement position is normally on or at a shaft bearing mounting position. Of course it is not actually on the shaft, but near enough for an accelerometer to detect the vibrations from the shaft through the bearing.
What is a balance plane?
A balance plane is simply a position on a shaft that the centre of the shaft and the centre of gravity of the shaft are being matched. That is you are trying to achieve a zero imbalance at that position.
So what is the difference between a measurement position & a balance plane?
Sometimes the relationship between measurement positions and balance planes is misunderstood.
The Prosig DATS Balance Analysis software is a true multi-plane balance software suite.
That means there is no limit to the number of balance planes that can be defined.
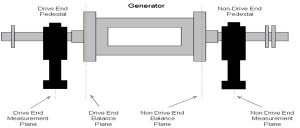
The diagram below shows two measurement positions, often called measurement planes and two balance planes.
Note that the measurement planes and the balance planes are not in the same position.
The rule that must be followed is that there must be at least one measurement plane for each balance plane.
To find out more about how Prosig can cover your balancing requirements take a look at…

Or to see the software in action…




James Wren
Latest posts by James Wren (see all)
- What Are dB, Noise Floor & Dynamic Range? - January 12, 2024
- How Do I Upsample and Downsample My Data? - January 27, 2017
- What Are Vibration, Torsional Vibration & Shaft Twist? - November 8, 2016


Please keep me updated on dynamic balancing of high speed rotors. Thanks.